Insect Pest Management: A Vital Strategy for Successful Farming
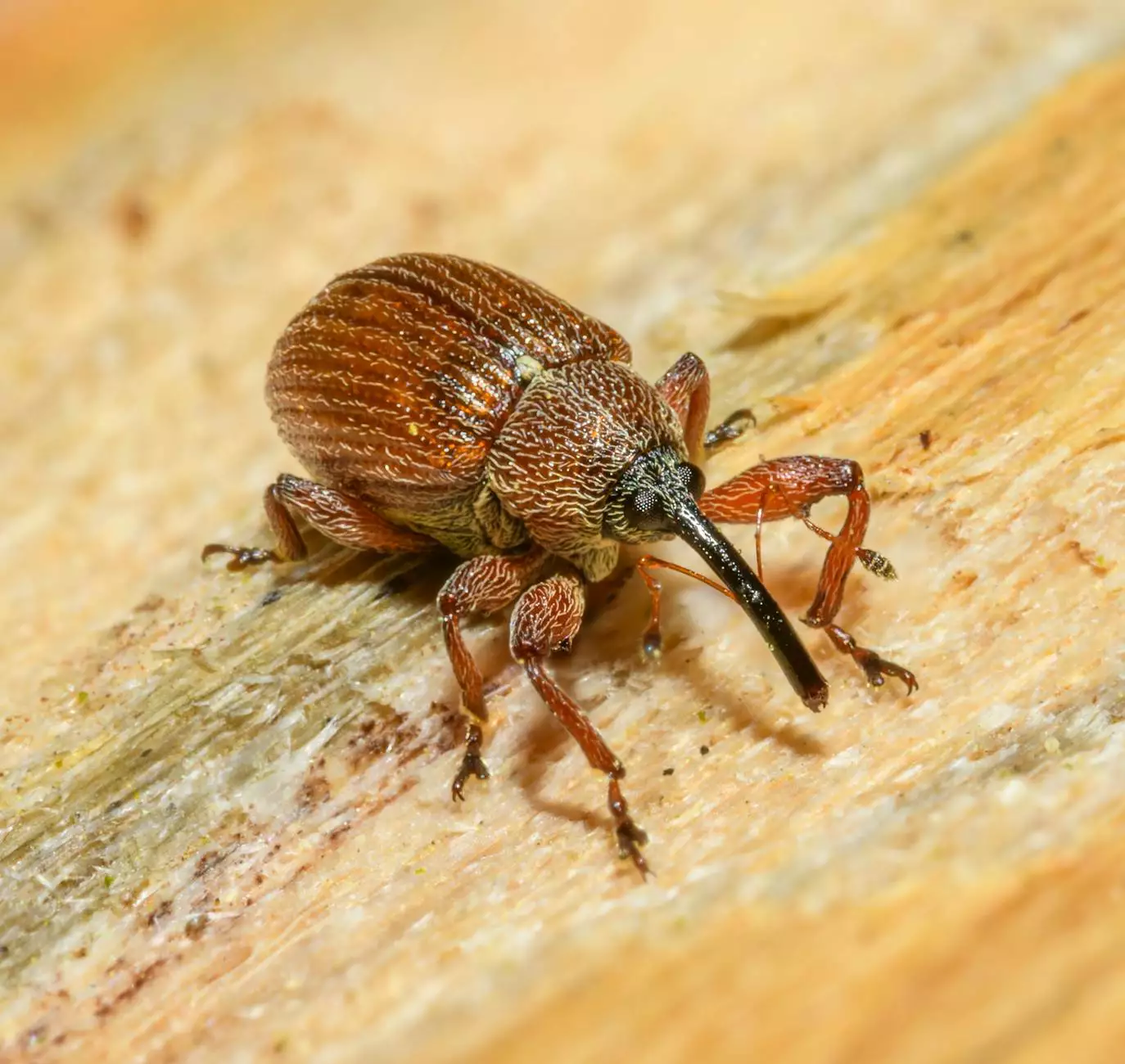

In the world of agriculture, the battle against pests is never-ending. Insects can wreak havoc on crops, leading to significant losses in yield and quality. Therefore, understanding insect pest management is crucial for farmers aiming to optimize their production and protect their investments. This article delves into various strategies, tools, and practices that can significantly reduce pest-related damage and promote healthier crops.
Understanding Insect Pest Management
Insect pest management (IPM) encompasses a range of strategies designed to control insect populations while minimizing the impact on the environment and non-target organisms. The goal of IPM is not merely to eliminate pests but to manage them effectively to reduce their populations to levels that do not cause significant economic harm.
Key Components of Insect Pest Management
Effective insect pest management combines several key components:
- Prevention: Implementing practices to deter pests before they become a problem.
- Monitoring: Regularly checking for signs of pest activity and assessing their populations.
- Identification: Recognizing the specific types of insects present to choose the most effective control methods.
- Control: Applying appropriate measures to reduce pest populations when thresholds are reached.
Importance of Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management is an advanced approach to managing insect pests that incorporates biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools in a way that minimizes economic, health, and environmental risks. By using IPM strategies, farmers can:
- Maximize crop yields by effectively controlling pest populations.
- Reduce reliance on chemical pesticides, leading to safer food production.
- Enhance biodiversity by allowing natural enemies of pests to thrive.
- Promote sustainable practices that protect the ecosystem.
Strategies for Effective Insect Pest Management
Implementing effective insect pest management strategies requires a multifaceted approach:
1. Cultural Control Practices
Cultural controls involve modifying farming practices to reduce pest establishment, reproduction, and survival. Examples include:
- Rotation of crops: Alternating the types of crops grown in a specific area can disrupt pest life cycles.
- Timing of planting and harvesting: Adjusting planting dates to avoid peak pest populations can reduce damage.
- Soil management: Healthy soils promote strong plant growth, making them less susceptible to pests.
2. Biological Control
Biological control utilizes natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to manage pest populations. Some examples include:
- Ladybugs: Effective against aphids.
- Parasitic wasps: Help control caterpillar pests.
- Fungi: Certain fungi can infect and kill targeted insect species.
3. Mechanical and Physical Controls
Mechanical and physical controls involve the use of barriers, traps, and other methods to prevent pests from reaching crops. Examples include:
- Row covers: Protects seedlings from insect damage.
- Traps: Sticky traps or pheromone traps can catch and monitor pest populations.
- Hand-picking: Physically removing larger pests, such as caterpillars, from plants can be effective.
4. Chemical Controls
While chemical controls should be used judiciously, they can be an important part of an IPM strategy. When applying chemical controls:
- Use targeted pesticides that are specific to the pest to minimize harm to beneficial insects.
- Follow label instructions for safe and effective application.
- Rotate chemicals with different modes of action to avoid developing pest resistance.
The Role of Technology in Insect Pest Management
Technology is revolutionizing the way farmers approach insect pest management. Innovations include:
- Drones: Allow for aerial monitoring of crops to assess pest activity and crop health.
- Mobile apps: Provide real-time pest identification and management recommendations.
- Sensors: Monitor environmental conditions to predict pest outbreaks based on weather patterns.
Developing a Successful Insect Pest Management Plan
To effectively implement insect pest management, farmers should develop a comprehensive plan:
1. Assess Your Farm's Needs
Identify the specific pests prevalent in your area and the crops you are growing. Understanding your unique challenges is crucial for developing an effective IPM strategy.
2. Monitor and Document Pest Activity
Regular monitoring is essential. Keep detailed records of pest occurrences, their life cycles, and the effectiveness of any control measures implemented.
3. Implement Control Strategies
Based on your monitoring data, implement the most appropriate control strategies, utilizing a combination of cultural, biological, mechanical, and chemical methods as needed.
4. Evaluate and Adapt
Evaluate the effectiveness of your efforts regularly and be prepared to adapt your strategies based on changing pest populations, crop conditions, and results.
Training and Education in Insect Pest Management
Continuous education is vital for farmers looking to enhance their insect pest management strategies. Consider the following:
- Workshops: Attend local extension service workshops focusing on pest identification and management techniques.
- Online Courses: Utilize available online resources and courses to further educate yourself on best practices.
- Networking: Connect with other farmers and pest management professionals to share experiences and learn from each other.
Conclusion: Building a Resilient Farming Future Through Insect Pest Management
In conclusion, effective insect pest management is integral to the success and sustainability of farming operations. By adopting an integrated approach that combines cultural, biological, mechanical, and chemical control methods, farmers can protect their crops, enhance their yields, and safeguard their investment. As challenges related to pests continue to evolve, staying informed, adaptable, and proactive is essential for building a resilient farming future.
For more information on insect pest management and how to integrate these techniques into your farming operations, consider consulting with experts in the field or visiting resources available at tsgcinc.com. By prioritizing pest management, farmers can ensure healthier crops and a more sustainable agricultural environment.